INTRODUCTION
Beekeeping is the maintenance of bee colonies for the purpose of collecting their honey, beeswax, flower pollination and more. Modern beekeeping attempts to revert to a less industrialized way of obtaining honey by utilizing smaller colonies, usually between 10,000 and 30,000 bees and the whole operation is based around the hive. Below we will teach you how to build a Langstroth hive which is common to North American and Australian beekeeping. This particular type of hive is customizable to the size of your colony which means you don’t need to build and plan out everything at the beginning of the journey. You can keep building and adding depending on how many bees you want. Below we will describe the parts of the beehive and the functions of each.
SUPPLIES
- Cut pine wood or bee box kits (see note)
- You will need the following components for a 10-frame Langstroth hive:
- 2 brood boxes and 3 super boxes (this is a starting point; some beekeepers use more, depending on their bees’ productivity)
- 10 frames per box
- 1 bottom board
- 1 inner cover
- 1 outer cover
- Wood glue and brush
- 6-penny nails
- Screws
- Hammer
- Clamps and square
- Paint (white or other light/pastel color)
- Nail gun (optional)
- Cordless drill/driver with driver and drill bits (optional)
- Frame assembly jig (optional)
Note: While you can cut your own pine wood to size for the boxes and frames, it’s usually also cost effective to buy kits. The kits come with precut wood pieces in the right dimensions, and they are often built to include finger joints that give extra strength to the box. Langstroth beehives can also be built slightly smaller, with eight frames.
DIRECTIONS
BUILD THE BROOD AND SUPER BOXES
Step 1: Brush wood glue onto the wood and join the edges of the boxes, making sure that the handles are on the outside if you are using a kit that offers built-in handles. This is an important step because wood swells as it ages, creating gaps. The glue helps solidify corners, ensuring the beehive can last several years. It’s common for a hive to remain in good condition more than 10 years.
Step 2: Use a hammer to ensure that all edges are well joined. Then attach clamps to the glued box and use a square to make sure the corners are perfectly squared.

Step 3: Nail the box together with a basic hammer or with a nail gun. You’ll want to make sure there is a nail at each finger joint, or about 36 in one brood box.
Step 4: Once the box is built, paint it with an exterior latex paint to protect the wood against the weather. White is the most popular color because it helps reflect light, which keeps the bee home cool in the summer. Other popular colors include pastels, like yellow, green and pink.

BUILD THE FRAMES
Step 1: If the kit has a piece (called a “wedge”) that snaps out of the top bar, remove it. Then brush wood glue onto the edges of the other pieces and stick them together. They should easily snap back snugly into place.
Step 2: Add a piece of foundation to the frame. The foundation is where the bees will do their work. They are frequently embossed with small honeycomb shapes that encourage the bees to use them. Each cell is the exact size needed for one egg to be laid and hatched. Foundations can be made from natural wax or plastic. They often have a waxy film on them.
Step 3: Reinstall the wedge, then nail all the sides together. Use shorter nails to reinforce the area around the wedge.

SETTING UP THE HIVE
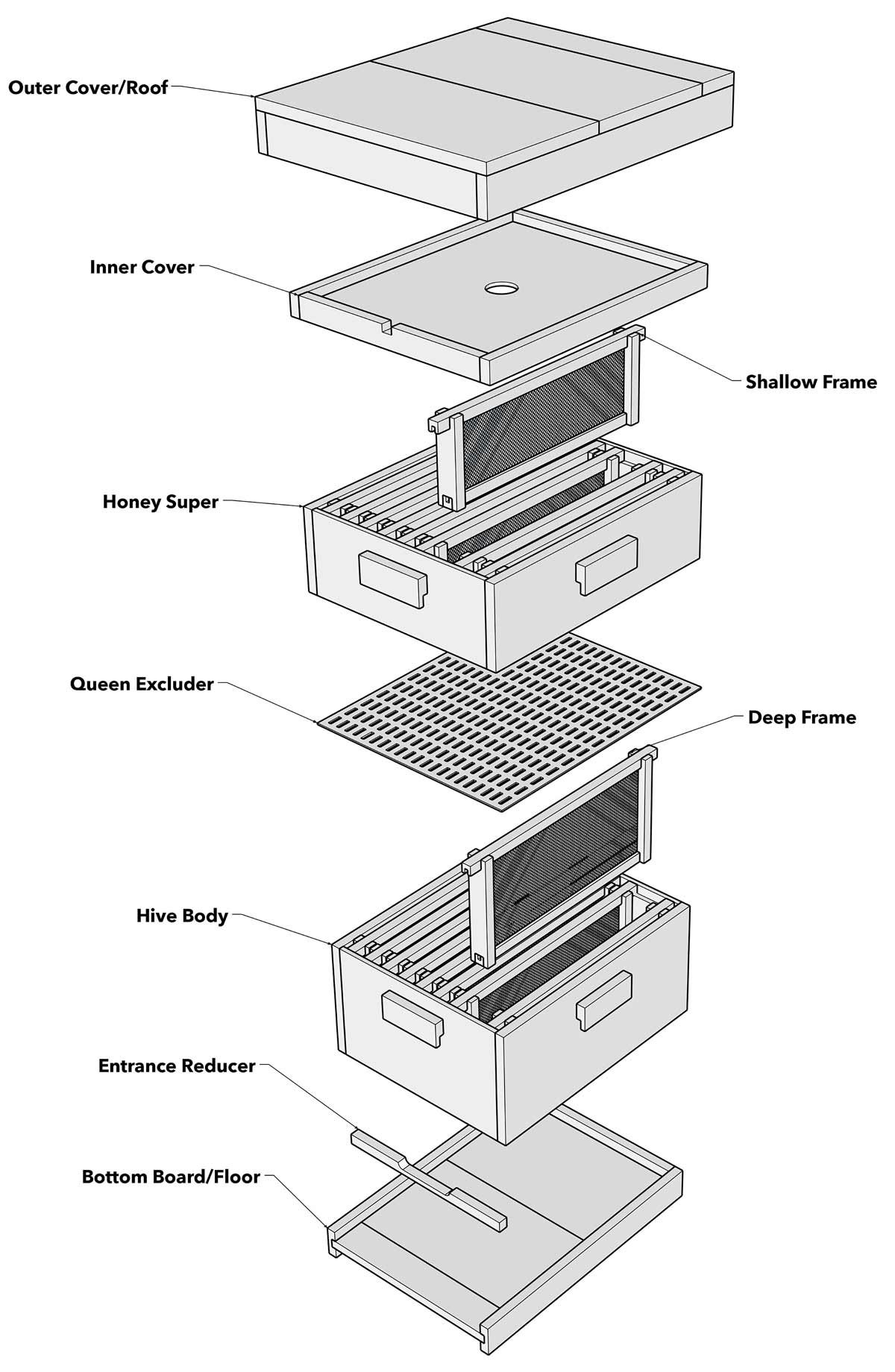
The Langstroth beehive, which is named after Rev. L. L. Langstroth — the father of American beekeeping and the mind behind this still-popular design, is made up of several boxes. Each is stacked on the other throughout the season as the bees become more productive.
Step 1: Place a “bottom board” on bottom. The bees will fly in and out of the hive through this board. When you have a young or small colony, you can install an “entrance reducer,” that restricts the entry space. This allows the bees to more easily protect themselves against intruders, like crickets and mice. Bottom boards can be purchased or made from a kit or from scratch.
Step 2: Place one of the brood boxes on top of the bottom board. Once you get bees, you will install them in this box. The queen bee will lay her eggs in the brood box, and worker bees will use it to store pollen and honey that the colony will consume.
Step 3: Place an “inner cover” over the brood box. This prevents the bees from completely sealing up the box. Place an “outer cover” on top of this. There are different types of outer covers. The one Charlie Canny uses is called a “telescoping cover.”
Step 4: Once you have installed bees, the setup is called an “apiary.” When the bees have filled the bottom brood box about 80 percent full, place another brood box on top. Once that box is 80 percent full, top it with a super box, which is slightly shorter than a brood box. Continue this process as much as needed. Beekeepers harvest honey from super boxes, which once full can weigh up to 60 pounds. Charlie Canny, Noble Research Institute director of facilities, and Pat Tickel, Texoma Beekeepers Association president, demonstrate how to use a kit to build two essential components of a beehive: brood boxes and frames. They are building a 10-frame Langstroth beehive, which will include two brood boxes, three smaller boxes called “supers,” and 10 frames per box.

Special thanks to Noble Research Institute and Family Handyman for the helpful resources and information on the topic of building beehives.
A portion of every purchase at Bee Kind Shop is donated to non-profit organizations that help save bee colonies around the globe.











